The Impact of Noise in Data Centers
The demand for cloud computing and data storage is growing, leading to more data centers being built in cities, suburbs, and rural areas. These facilities include equipment that can produce significant noise, including electrical generators, ventilation equipment, cooling equipment, and are often built near residential, educational, medical, or other sensitive areas. It is important to control this noise in order to meet noise regulations and be a good neighbor.
Key factors in arriving at a suitable noise control strategy typically include:
- Type of equipment causing the noise disturbance, including any need for ventilation and/or heat dissipation.
- Proximity between the equipment and the nearest neighbors, considering the local noise ordinances or existing ambient conditions without the data center.
- Ease of access to the equipment for maintenance or replacement; and of course, cost. Noise control strategies may include sound attenuating enclosures, exhaust mufflers, ventilation silencers, noise barrier walls, or other strategies.
EEA’s ANV team is capable of identifying the key pieces of equipment to target for noise control based on acoustical and/or vibration measurements taken on-site and/or review of equipment operating parameters. The most suitable noise control strategy for a particular project is determined based on this analysis and interaction with Design/ Construction teams and end-users

Three case studies are presented to illustrate how noise from data centers can be managed in urban, suburban, and rural settings. These studies highlight the importance of evaluating noise levels and implementing measures to reduce noise disturbance for nearby residents and businesses.
Urban Industrial District Data Center
Location: Urban area with nearby sensitive facilities like a child care center and office spaces.
Equipment: Four generators inside the building with louvers for air intake and exhaust.
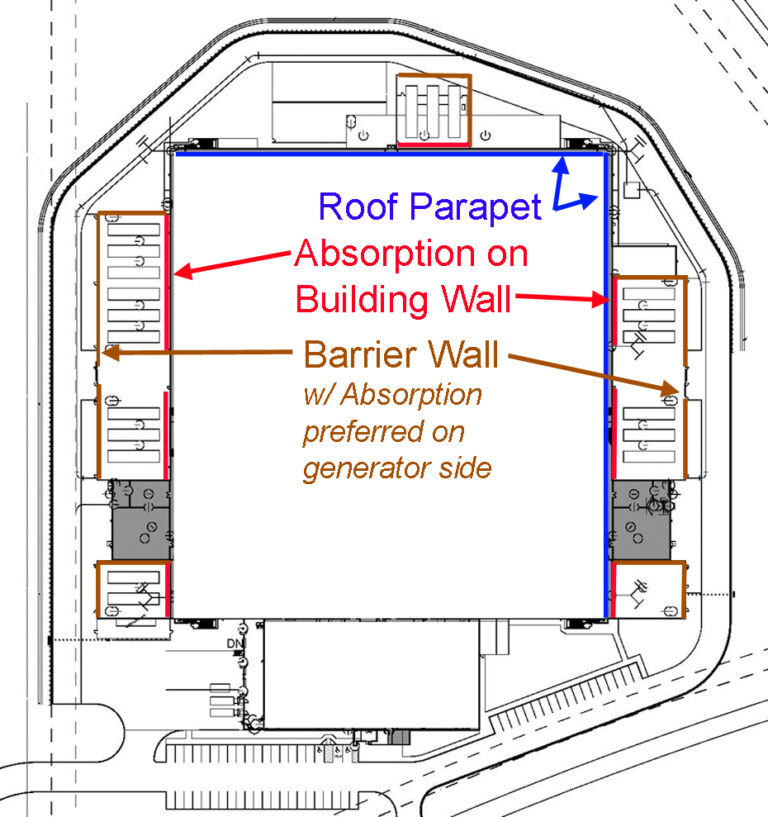
Recommendations: Install sound attenuating louvers, use high-performance exhaust mufflers, and apply acoustic finishes to reduce noise.
Suburban Commercial-Industrial District Data Center
Location: Suburban area near residential and commercial buildings with hilly terrain.
Equipment: Twenty generators placed outdoors in clusters, along with ventilation units on the roof.
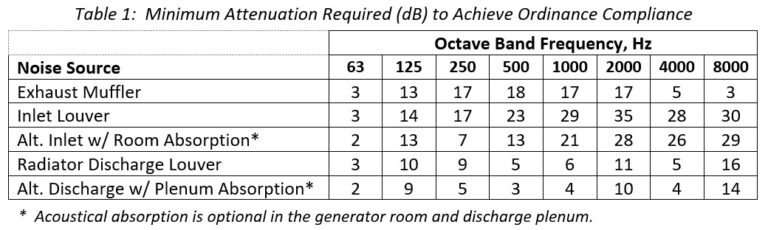
Recommendations: Enhance air intake and exhaust attenuators, upgrade engine mufflers, and consider installing walls around generator clusters to reduce noise.
Exurban Location Data Center
Location: Rural area with flat terrain, adjacent golf course, distant homes and farmhouses, and some nearby wooded areas and wetlands.
Equipment: Numerous generators distributed across multiple buildings, with ventilation units on the roof.
Recommendations: Use sound baffles, insulated exhaust plenums, and intake relief openings with louvers to control generator noise.

Overall, each case study highlights different challenges in managing noise from data centers based on their location and surrounding environment. Solutions include implementing soundproofing measures and ensuring compliance with noise regulations to minimize disturbance to nearby residents and businesses.
Have questions or want to learn more? Contact us below!